News Green steel quotas for CO2 emissions 1998 25 April 2025
Prices for CO2 emission permits returned to growth after a localized low in the first half of the month
The cost of European CO2 emission allowances (EUAs) rose from €60.8/t to €66.9/t from April 9 to 23, according to Trading Economics. This is €3.8 less than at the beginning of the month. The lowest price in the EU ETS trading system was recorded on April 9.
Overall, the decline in the emissions price in April coincides with a drop in natural gas prices in the EU, which is due to a seasonal factor – the end of the heating season. From April 1 to April 23, spot gas prices on the TTF exchange fell from €446/1000 m3 to €358/1000 m3.
In 2024, greenhouse gas emissions in the EU decreased by 5%. According to the European Commission, this is due to an 8% increase in electricity production from renewable energy sources and a 5% increase in nuclear energy. At the same time, electricity production at coal-fired power plants decreased by 15% and at gas-fired power plants by 8%.
Emissions in the industrial sector remained stable. A 5% reduction in the cement industry was offset by a 7% increase in emissions in the chemical industry (fertilizer production).
Emissions in the European steel industry are declining along with production cuts. In January-March, steel production in the European Union decreased by 2.5% y/y – to 32.4 million tons. At the same time, the decline stopped in March, with a 0.2% year-on-year increase – to 11.7 million tons.
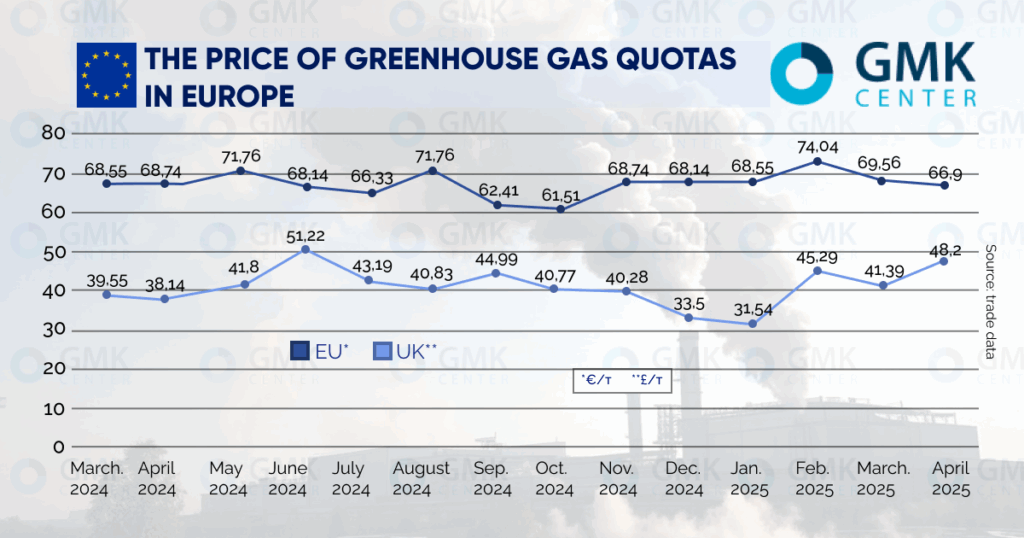
British futures for CO2 emissions on the London ICE exchange this month rose from £45.9/t to £48.2/t as of April 23. At the same time, as in the EU ETS, the local minimum was recorded on April 9 at £41.2/t.
The rise in price may be due to a situational increase in demand from coal-fired power plants. In the UK, they account for slightly more than 5% of electricity generation, but traders can rely on these requests as an indicator.
As reported, in March 2025, Chinese steel mills increased their emissions by 9.7% y/y. At the same time, emissions of sulphur dioxide, particulate matter and nitrogen oxides in exhaust gases decreased by 13.1%, 5.5% and 16%, respectively.



